What does artificial intelligence actually mean? Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a technology that allows computer systems and machines to simulate intelligence - allowing them to perform tasks, solve problems, take decisions, create, learn and more.
This article will break down AI step-by-step, from what it is and how it works, to its history, benefits, and challenges. If you are completely new to the subject, by the end you'll have a clear understanding of what AI is and why it matters.
What is AI in Simple Terms?

In simple terms, artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines and computers to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. For example, recognising patterns, making decisions, learning from data, and solving problems.
Think of AI like a super-smart assistant that learns from experience instead of a machine programmed to perform every single task. Note: Machine Learning (ML) models are HOW the machine or computer learns, and in essence what makes an AI "intelligent".
What Do People Mean When They Say "AI" Today?
Today, when people talk about AI, they usually mean a futuristic automation or technology with almost human-like thinking. For example, they might think of AI robots from Terminator or iRobot. In reality, AI is a set of algorithms (set of instructions) trained to perform specific tasks based on data, rather than robots with human-like brains capable of showing emotions or showing independent thoughts while solving problems (at least for now).
More realistic examples of current AI today include self-driving cars, Netflix and Spotify giving recommendations based on what you watch, or image generators based on a prompt. These are more machine learning (ML) and deep learning examples, which are specific branches of AI.
Why Do We Need AI?
AI makes our life easier, faster and smarter. We live in a Digital Age derived from the Information Age which started mid-20th century with the development of computers and the rise of the internet. Nowadays, there is too much information for humans to process manually.
AI helps us by handling complex problems which involve analysing tons of data, automating processes, and offering predictions. Here are other reasons why AI is essential:
- Efficiency: AI automates tasks, saving us time and effort.
- Accuracy: AI reduces human errors, whether it's diagnosing diseases or detecting fraud.
- Innovation: AI enables discoveries, like finding new medicines or optimising systems.
- Scalability: AI works on problems that are too big for humans to tackle, such as managing global supply chains or analysing climate data.
This does not mean that AI will replace humans at all, but assist them in progressing faster and more efficiently in the same way a calculator helps in performing calculations faster or the internet which reshaped communication.
How Does AI Work?
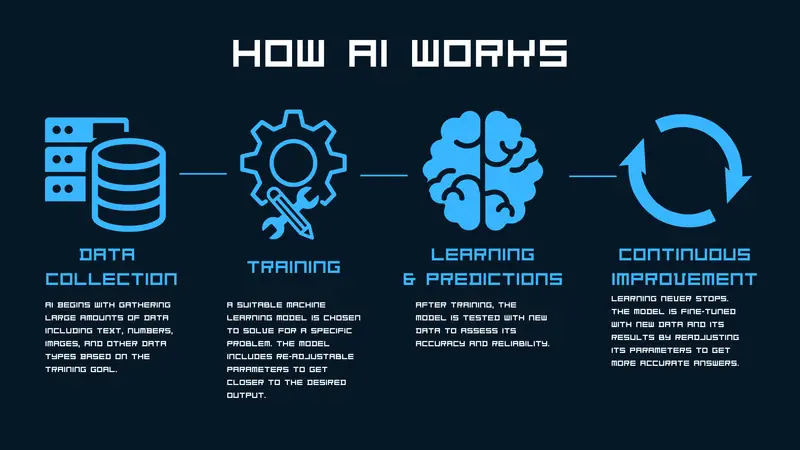
In summary, AI works by combining data algorithms, and computational power. Below there is a quick breakdown summarising how AI works, if you want a more in-depth answer visit How AI Works .
- Data Collection: Data (e.g. photos, text, numbers) is collected and fed to an AI training system (e.g. a machine learning model).
- Training: The AI system learns patterns from this data using algorithms (like neural networks).
- Learning & Predictions: AI predicts or makes decisions based on what it's learned.
- Continuous Improvement: AI adjusts its answer as it processes more data and gets better overtime.
Think of it like training a dog: give it commands (algorithms/instructions), reward good behaviour (feedback), and it will eventually learn to perform tasks on its own. The objective is to reduce the margin of error.
Examples and Uses of AI
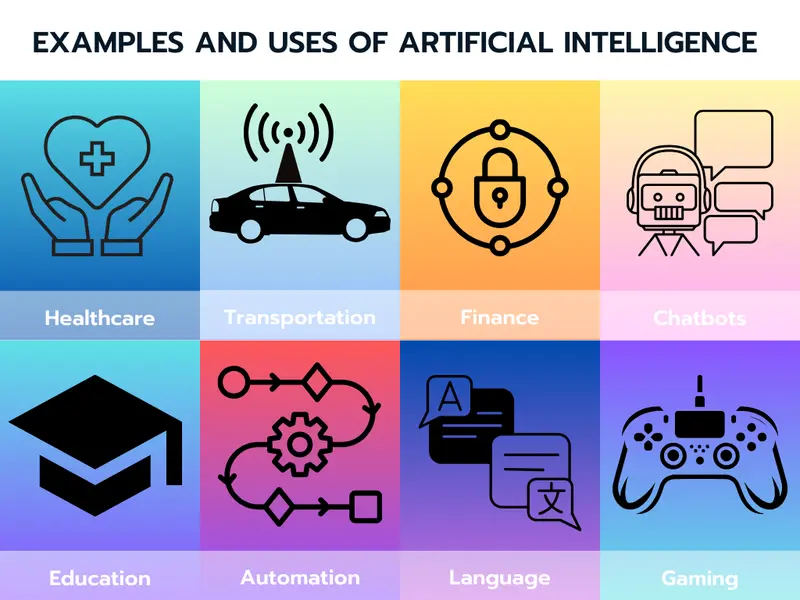
Here are some real-life examples by industry on how AI is used:
- Healthcare: AI analyses medical images to assist in diagnosing diseases like cancer.
- Transportation: AI-powered navigation systems optimise routes and traffic management.
- Finance: AI algorithms detect fraudulent transactions in real-time.
- Customer Service: AI chatbots handle common inquiries and support requests.
- Gaming: AI creates adaptive and challenging opponents in video games.
Types of AI
There are three types of AI based on capabilities and other four types of AI based on functionalities all listed briefly below. If you want a more in-depth answer of how each type of AI differs visit Types of AI .
Types of AI based on capabilities:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Designed for specific tasks, like voice assistants or recommendation systems.
- General AI (Strong AI): Hypothetical AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can do (it doesn’t exist yet).
- Super AI: AI that surpasses human intelligence (still theoretical).
Types of AI based on functionalities:
- Reactive Machine AI: Focuses on responding to specific stimuli with predefined actions. It doesn't retain memories or learn from past experiences (e.g. Deep Blue chess computer).
- Limited Memory AI: Can use historical data to make decisions and improve over time but only retains information for a short period (e.g. self-driving cars).
- Theory of Mind AI: A theoretical type of AI that understands emotions, beliefs, and intentions of others, enabling it to interact more naturally (still in development).
- Self-Aware AI: Also theoretical, this type of AI has its own consciousness and awareness, capable of introspection and understanding its own existence (just a dream for now).
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI
Like any technology, AI has its pros and cons. Let’s break it down:
Advantages
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks.
- Cost-Effective: Saves money over time by reducing manual labor.
- Accuracy: Minimizes errors in critical fields like medicine and finance.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike humans, AI doesn't need breaks.
Disadvantages
- Job Losses: Automation could replace certain jobs.
- Bias: If trained on biased data, AI can make unfair decisions.
- Lack of Creativity: AI lacks human emotions and creativity.
- Expensive to Build: Developing and maintaining AI systems can be costly.
History of AI
Who Created AI?
The creator of AI was Alan Turing, a British mathematician and computer scientist, laid the groundwork for AI by asking, “Can machines think?” in the 1950s. He introduced the Turing Test which evaluates a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behaviour indistinguishable from a human.
When was AI Invented?
The official birth of AI as a field of study was in 1956, during a conference at Dartmouth College. This event, led by John McCarthy (who coined the term “artificial intelligence”), Marvin Minsky, and others, marked the start of serious research into building machines capable of reasoning and learning.
Why was AI Created?
AI was created to solve problems that were too complex or time-consuming for humans to handle. Early researches dreamed of building systems that could think, learn and improve overtime. The goal here was to improve quality of life and solving some of humanity's biggest challenges.
What is the Future of AI?

AI's future is exciting, but also very uncertain. Here are a few predictions and possibilities:
- More Advanced AI Systems: AI will continue to become smarter, handling even more complex tasks like designing drugs, writing novels, or diagnosing rare diseases.
- Integration with Everyday Life: We’ll see AI deeply embedded in our homes (smart devices), workplaces, and cities (smart infrastructure).
- Ethical Challenges: The future of AI will require careful consideration of ethics, privacy, and regulation to ensure it benefits society.
- Job Transformation: While some jobs may be automated, new AI-related careers will emerge, requiring up-skilling and education.
- AI and Creativity: Systems like ChatGPT are already showing creative potential. In the future, AI may co-create art, music, and literature alongside humans.
Conclusion and Takeaways
Artificial intelligence is a reality now, not just science fiction, and it's changing how we live today. From automating tasks to assessing enormous amounts of data, AI has become a powerful tool in human progress.
To recap:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines to perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence.
- AI works by learning from data and improving over time.
- We need AI because because nowadays there is too much information for a human to handle. AI helps by handling complex problems faster, improve efficiency, and innovate.
- AI has its pros (e.g. accuracy, efficiency) and cons (e.g. job displacement, bias).
- Some of the first AI pioneers were Alan Turing and John McCarthy in the 1950s.
It is important to remember that AI is a tool. How we use it will determine whether it becomes a good force or source of concern.