We're exploring the different types of AI that are now part of our everyday lives. We'll look at how each type of AI, from narrow AI to Super AI, is made to do specific jobs well such as assistants like Amazon's Alexa and Apple's Siri to IBM Watson.
Key Takeaways
- There are two main types of AI: Capability-based AI and Functionality-based AI.
- We can divide capability-based AI into three main types: Narrow AI (ANI or Weak AI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI or Strong AI), and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI or Super AI).
- Artificial General Intelligence and Artificial Superintelligence are theoretical types of AI.
- We can divide functionality-based AI into four main types: Reactive AI, Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI, and Self-Aware AI.
- Theory of Mind AI and Self-Aware AI are theoretical types of AI.
- Existing examples of Narrow and Limited Memory AI include ChatGPT, the Netflix recommendation engine, and the Siri virtual assistant, among others.
What Are The Main Categories of AI and How do They Differ From Each Other?

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has grown into two main types: capability-based AI and functionality-based AI. Knowing these categories helps us see how they are used and improved in tech.
- Capability-based AI looks at how well AI can do tasks. For example, Narrow AI is used in about 99% of AI today (more below). It's good at things like recognising faces or searching the internet. This is different from Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which tries to be as smart as humans but is still just an idea.
- Functionality-based AI sorts systems by how people use them and what data they process. This way, we can see how AI is used in areas like healthcare, transportation, and shopping. For example, self-driving cars and chatbots in customer service are becoming more common.
Theory of mind AI and self-aware AI are still theoretical or in-development. About 30% of AI experts think we can get theory of mind AI in 15 to 20 years. But self-aware AI is still mostly a dream, with not many thinking it's possible soon.
Now let's talk about these types their AI subcategories in more detailed:
Capability-Based Types of AI
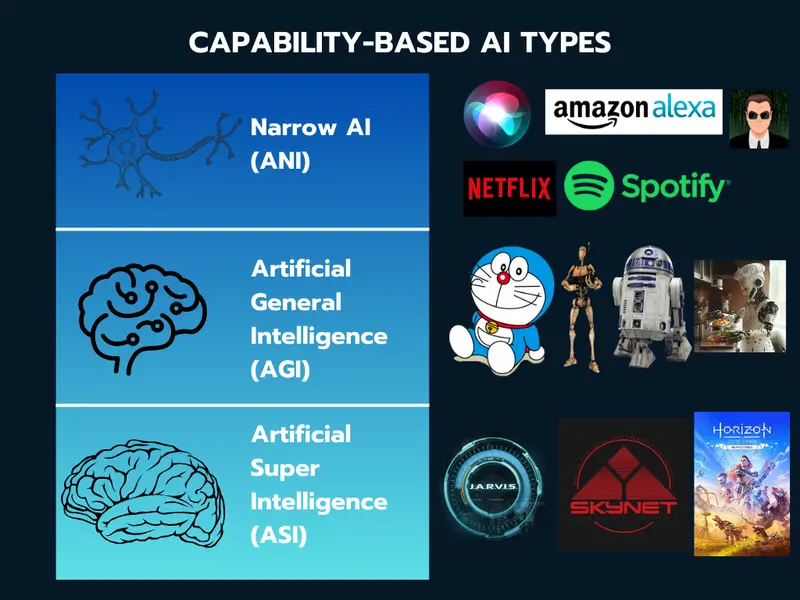
We can divide capability-based AI into three main types: Narrow AI, Artificial General Intelligence, and Artificial Superintelligence. Each type has its own features and uses. We'll look at each one below.
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, or Weak AI, is the most common AI today. It's made to do specific tasks. For example, Siri and Alexa use narrow AI to understand and respond to users.
Thanks to machine learning, narrow AI has gotten much better. It's now used in healthcare to help diagnose diseases accurately.
Examples of Narrow AI include:
- Siri and Alexa virtual assistants
- Netflix and Spotify recommendation engines
- Waze and Google Maps enhanced navigation
- Chess.com AI computers
Artificial General Intelligence (Strong AI)
Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI, is still just an idea. It aims to be as smart as humans in many areas. AGI would use advanced tech to think like us.
Even though AGI is not here yet, it drives a lot of research. It makes us think about what it means for machines to be as smart as us.
Examples of Artificial General Intelligence (Strong AI) include:
- A robotic housekeeper that can learn any household task just like a human
- An AI researcher that can design and conduct its own experiments
- A robotic chef that can create new recipes and adapt its cuisine
Note that this examples are just hypothetical due to its speculative nature.
Artificial Superintelligence (Super AI)
Artificial Superintelligence, or Super AI, is the most dreamy AI idea. It's about machines being smarter than humans in everything. This idea is still just a dream, but it's exciting and a bit scary.
Going from AGI to superintelligence makes us think about ethics. It makes us wonder what it means to create something smarter than us.
Examples of Artificial Superintelligence (Super AI) include:
- A climate control AI that can manage earth's entire ecosystem
- An AI system that could solve all known mathematical problems
- A medical AI that could cure any disease by understanding its biological process
Note that this examples are just hypothetical due to its speculative nature.
Functionality-Based Types of AI

Knowing about AI's functionality shows us how wide its uses are. We look at two main existing types: reactive AI and limited memory AI. Although there are other two theoretical types (theory of mind AI and Self-aware AI). Each has its own special abilities.
Reactive Machine AI
Reactive AI is the simplest form of AI. It works only with current data and can't learn from past experiences. IBM's Deep Blue, which beat chess world champion Garry Kasparov in 1997, is a great example. It made decisions based only on what it knew at that moment.
Examples of Reactive Machine AI include:
- Deep Blue chess computer
- IBM's Watson
- Single game opponents
Limited Memory AI
Limited memory AI is a more advanced type of AI. It keeps and uses past data to make better choices. Self-driving cars are a good example. They learn from their surroundings to get better at navigating roads.
As we learn more about AI, we see reactive AI as a starting point. Limited memory AI is a step up, leading to even more AI progress in the future.
Examples of Limited Memory AI include:
- Self-driving cars
- Chatbots like ChatGPT
- Recommendation algorithms (e.g. Netflix, Spotify)
- Virtual assistants (e.g. Siri, Alexa)
Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI is designed to understand emotions, beliefs, and intentions of others. This type of AI mimics human understanding of social and emotional cues. In theory, it would enable machines to interact with humans in a more natural and intuitive way. For example, AI in robotics could learn to recognise when someone feels upset or happy, adjusting its responses accordingly.
This level of cognitive sophistication is still in development but holds potential for more empathetic interactions between machines and humans. Training AI models for this purpose is an interesting challenge, as it involves feeding the model large amounts of data which for this case might include social interactions, language, and emotional cues.
Examples of Theory of Mind AI include:
- Empathetic caregiving robots
- AI therapists that understand emotions
- AI teachers that adapt to students' mental states
Note that this examples are just hypothetical due to its speculative nature.
Self-Aware AI
Self-aware AI is the most advanced type, possessing consciousness similar to humans. It doesn't just understand the world around it, but also has an awareness of its own existence and emotions. This AI could evaluate its actions and modify its behaviour based on internal reflections.
While still theoretical, self-aware AI would be able to think, reason, and understand its own intentions, opening the door to entirely new possibilities in automation and intelligent systems.
Examples of Self-Aware AI include:
- Any AI system with genuine consciousness, morality, ambitions, and self-preservation instincts.
Note that this examples are just hypothetical due to its speculative nature.
What Are The Different Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
To recap, let's summarise the different types of AI we've covered.
Capability-based AI is split into three main types:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): Focuses on specific tasks without learning capabilities. Also known as Weak AI.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Has basic human thinking skills and can learn. Also known as Strong AI - still theoretical.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): Seeks to surpass human thinking abilities. Also known as Super AI - still a speculation.
Functionality-based AI has four notable types:
- Reactive Machines: Simple tasks without learning, like IBM Deep Blue.
- Limited Memory: Uses past data for better predictions, seen in self-driving cars.
- Theory of Mind: Aims to understand human feelings - still theoretical.
- Self-aware AI: Still in science fiction, not yet possible.
Knowing how AI is classified helps us see the differences between various types. This knowledge is key to understanding the impact of AI on our world.
| AI Type | AI Category | Short Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow AI (ANI) | Capability-based | Narrow AI (Weak AI) designed to perform specific tasks. | Siri, Google Translate, Chess AI, Spam Filters, Weather Prediction Systems |
| Artificial General AI (AGI) | Capability-based | General AI (Strong AI) capable of understanding and performing any intellectual task a human can. | Fictional examples: HAL 9000, Data (Star Trek), The Machines in "The Matrix" |
| Superintelligent AI (ASI) | Capability-based | Superintelligent AI (Super AI) surpassing human intelligence in all aspects. | Fictional examples: Skynet, Ultron, Gaia (Horizon games) |
| Reactive Machines AI | Functionality-based | Reacts to current inputs without memory or past context. | Deep Blue, Self-driving car sensors, Recommendation Systems |
| Limited Memory AI | Functionality-based | Uses past data for decision-making but cannot store it permanently. | Virtual assistants, ChatGPT, Autonomous Vehicles, Image Recognition Systems |
| Theory of Mind AI | Functionality-based | Understands emotions, beliefs, and social interactions. | Fictional examples: Baymax (Big Hero 6) |
| Self-aware AI | Functionality-based | Possesses consciousness, self-awareness, and independent reasoning. | Fictional examples: Eva (Ex Machina), Ava (I, Robot) |
What is the Difference between an AI Type and AI Model?
Many mix up AI types with AI models. The difference between these terms is that AI types group systems by what they can do, while AI models are specific designs for tasks like recognising patterns and creating algorithms.
Getting to know AI terms is key for those exploring artificial intelligence. We often see AI types and AI models, which seem similar but are not. For instance, Narrow AI is a type of AI that uses machines learning models to perform specific tasks such as voice recognition.
Knowing the difference helps us pick the right tools for our tasks. This knowledge helps us use AI in practical ways.